Thermal imaging technology is revolutionizing the way we perceive and interact with our surroundings. These devices can detect infrared radiation emitted by objects in their field of view and convert that data into thermal images. They are used across a wide range of industries, from building inspection to firefighting, electrical maintenance, and even medical applications.
How Does a Thermal Imaging Camera Work?
Thermal imaging cameras work by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by objects in their field of view. Infrared radiation is invisible to the human eye but can be detected by the thermal camera's sensor. The camera then translates the data it receives into a thermal image that can be displayed on a screen, providing a visual representation of temperature differences in the scene. The temperature of objects in the scene is represented by different colors in the thermal image. By analyzing the thermal image, the user can identify temperature differences in the scene, which can be used for a variety of purposes.
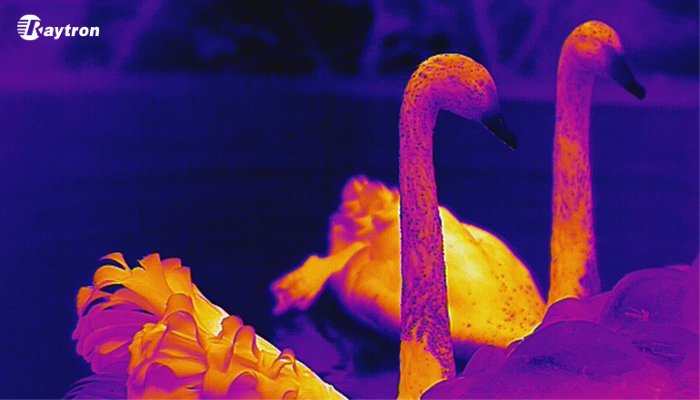

Applications of Thermal Imaging Cameras
Thermal imaging cameras have a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most common uses include:
Building Inspection: Thermal imaging cameras can detect areas of energy loss, moisture intrusion, and insulation defects in buildings. By identifying these areas, building inspectors can recommend energy-efficient improvements that can reduce heating and cooling costs.
Electrical Maintenance: Thermal imaging cameras can detect electrical faults such as loose connections, overheating, and overloading in electrical systems, helping to prevent electrical fires.
Firefighting: Thermal imaging cameras can help firefighters locate hotspots and people in smoke-filled environments, improving their ability to navigate and respond to emergencies.
Medical: Thermal imaging cameras can detect differences in skin temperature that can help identify early signs of inflammation or disease.
Research and Development: Thermal imaging cameras are used in a variety of scientific research and development applications, including materials science, biology, and aerospace engineering.

Types of Thermal Imaging Cameras
There are two main types of thermal imaging cameras: uncooled and cooled. Uncooled thermal cameras use a microbolometer detector that is sensitive to infrared radiation and can operate at room temperature. Uncooled thermal cameras are ideal for a wide range of applications, including building inspection, electrical maintenance, and firefighting.
Cooled thermal cameras use a more sensitive and expensive detector that requires cooling to operate effectively. They are typically more accurate and can detect smaller temperature differences than uncooled thermal cameras. However, this type of thermal camera is also more expensive and requires more maintenance. Cooled thermal cameras are typically used in research and development applications, where high accuracy is essential.
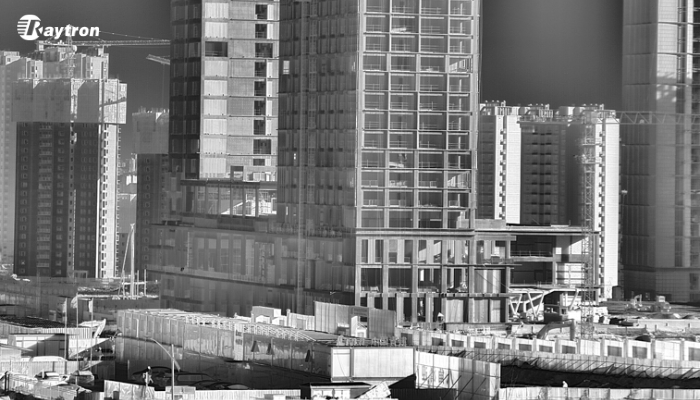

Buildings taken by Raytron 1280 cooled infrared thermal imaging camera
Recent Advances in Thermal Imaging Technology
Thermal imaging technology is constantly evolving, and there have been many recent advances in the field.
One such advancement is the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms. This kind of thermal camera system has been developed that can analyze thermal images and has the ability to recognize patterns and anomalies. These algorithms can be used to detect early signs of disease, identify energy inefficiencies in buildings, and even detect objects in darkness.
Another recent advance in thermal imaging technology is the development of thermal cameras that can directly attach to smartphones or tablets. These devices are small, affordable, and easy to use, making them ideal for home inspections and other applications.