Guarding the Wild 24/7: How Infrared Thermal Camera is Saving Endangered Species in Total Darkness
As ecosystems face unprecedented pressures, the demand for non-invasive, high-precision monitoring tools has never been higher. Among these innovations, thermal imaging has emerged as a powerful force, enabling a more sustainable and scientifically rigorous approach to animal protection. By moving beyond traditional observation methods, this technology is helping to facilitate a deeper understanding of the natural world while adhering to the strictest ethical standards of conservation.
Night Vision VS. Thermal Imaging: Which to Choose?
Conventional night vision devices rely on amplifying ambient visible or near-infrared light, making their performance highly dependent on moonlight or artificial illumination. In contrast, thermal cameras detect the heat radiation emitted by animals and humans themselves.
This allows infrared systems to function in complete darkness, through foliage, fog, or light rain—delivering consistent situational awareness in complex natural environments. For wildlife monitoring and anti-poaching operations, this fundamental technical advantage makes thermal imaging a preferred tool over standard night-vision optics. From a social perspective, thermal monitoring is increasingly used to mitigate human–wildlife conflict, a pressing challenge in regions where expanding agriculture intersects with animal migration routes. When thermal cameras detect large mammals approaching farmland or villages, early-warning systems can alert rangers and residents in advance, allowing non-lethal deterrence measures to be deployed. This prevents crop damage, protects rural livelihoods, and reduces the risk of injury or death for endangered species—creating a more balanced coexistence between people and wildlife.
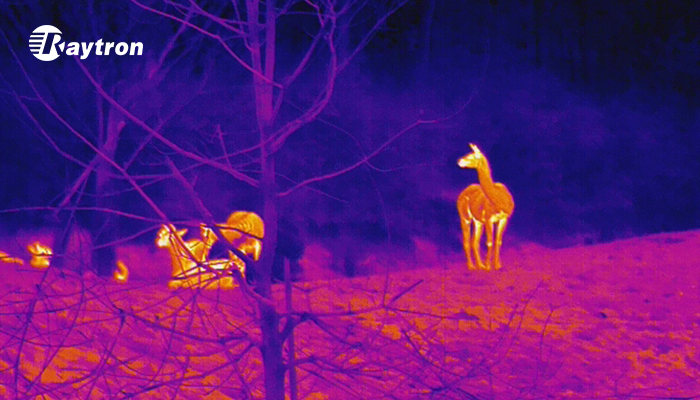

The Advantages of Infrared Thermal Cameras in Ecological Monitoring
Infrared Thermal Imaging for Wildlife Observation
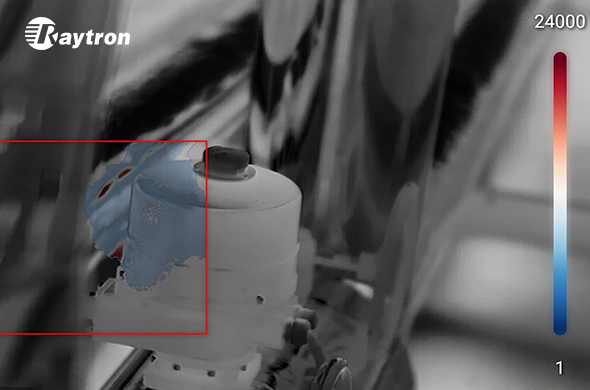
The core challenge of wildlife conservation has always been the "observer effect", the risk that human presence or artificial lighting will disrupt the natural behavior of the species being studied. Thermal imaging for wildlife observation eliminates this obstacle by allowing researchers to monitor animals through their heat signatures rather than visible light. Because infrared sensors detect long-wave infrared radiation, they provide a 24/7 window into the natural world that remains effective in total darkness, dense fog, or thick canopy cover. This level of visibility is crucial for tracking nocturnal species or monitoring migratory patterns without introducing stress-inducing elements like flashlights or heavy human patrols.
Furthermore, the integration of thermal technology into anti-poaching efforts has become a cornerstone of modern habitat security. High-sensitivity thermal sensors can distinguish the thermal profile of humans from the surrounding environment at significant distances. This proactive capability allows rangers to identify unauthorized activities in protected areas long before a physical confrontation occurs, effectively creating a "digital fence" that operates around the clock. By providing clear visual evidence in challenging conditions, infrared technology serves as both a deterrent and a vital tool for the legal protection of endangered habitats.
How Does Infrared Technology Contribute to Ecological Conservation?
Different thermal imaging platforms serve complementary roles in ecological monitoring:
· PTZ thermal systems provide 360-degree coverage across large territories and are commonly deployed along park perimeters and high-risk corridors.
· Thermal monoculars enable mobile rangers to track animals at long distances and estimate range in the field.
· Thermal-equipped civilian drones extend situational awareness from the air, allowing authorities to monitor herds, terrain, and movement routes rapidly.
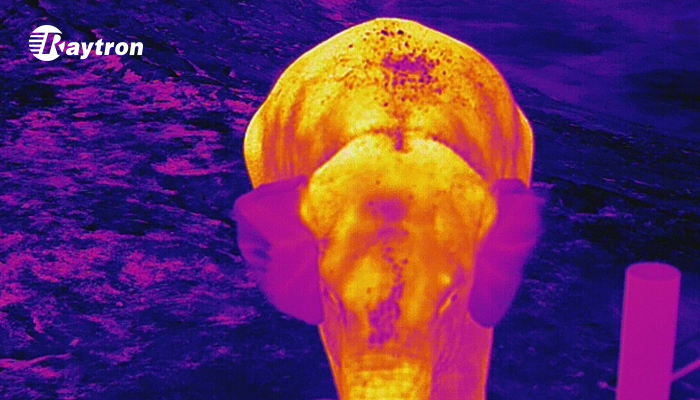
In Yunnan Province, China, infrared imaging systems supplied by Raytron have been deployed to assist authorities in monitoring Asian elephant migration routes, providing real-time situational awareness during large-scale movements and helping guide traffic control and community safety measures. These real-world deployments illustrate how thermal sensing can transform ESG principles into measurable environmental and social outcomes.
About Raytron
As a trusted global provider of infrared thermal technology, Raytron believes that meaningful innovation must advance environmental protection and social well-being at the same time. Through energy-efficient infrared sensors and AI-enabled “Smart Thermal Imaging Systems,” Raytron supports long-term biodiversity monitoring in remote habitats while minimizing environmental impact—directly aligning with the Environmental pillar of ESG. These solutions also help authorities and local communities reduce human–wildlife conflict through early-warning detection and migration monitoring, protecting livelihoods while safeguarding endangered species. Guided by rigorous ESG standards and a commitment to ethical innovation, Raytron is dedicated to making wildlife protection safer, more accurate, and more sustainable—ensuring that thermal technology contributes not only to technological progress, but also to the preservation of the planet’s natural heritage for generations to come.