The adoption of thermal imaging for vehicles is transitioning from a luxury offering to a potential safety necessity. According to the Thermal Imaging and Sensing Report 2025 from Yole Group, approximately 200,000 thermal imaging cameras were integrated globally in 2023, primarily in high-end models. However, as highlighted in their analysis of the IR thermal imaging market trends for automotive applications, the sector is poised for substantial growth, with projections pointing to a market reaching millions of thermal imaging units annually by 2029.
The primary catalyst is the global emphasis on improving Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB), particularly for pedestrian protection. Leading safety rating agencies such as Euro NCAP and the IIHS have consistently highlighted the weak nighttime performance of camera- and radar-based AEB systems. The identified shortfall creates a major opportunity for automotive thermal cameras for ADAS integration. Thermal imaging sensors provide reliable heat-based detection independent of light, directly addressing the core failure mode in current systems. As future mandates for more reliable pedestrian AEB could trigger widespread automotive thermal camera adoption, the industry is closely monitoring regulatory trends.
The Unique Advantage of Automotive Thermal Imaging for Nighttime Safety
At night, in poor weather conditions, or against sudden glare, the performance of both human drivers and camera-based ADAS systems drops significantly. This creates a dangerous gap where pedestrians, animals, and obstacles become difficult to identify in time to prevent a collision. Thermal imaging technology provides a decisive solution to this problem. Passively detecting the infrared heat signatures emitted by all objects above absolute zero degrees creates a clear image independent of visible light. This capability ensures reliable detection when it is needed most, forming a foundational layer for true 24/7 safety.
The core principle of thermal imaging—detecting long-wave infrared radiation emitted by objects—enables vision in total darkness. However, for automotive safety, the critical challenge is maintaining a strong, interpretable signal at the necessary long range (250-300m). Raytron addresses this by engineering high-sensitivity infrared detectors paired with advanced thermal picture processing algorithm. This combination ensures that the camera's output provides not just a “detection,” but a clear, reliable thermal signature at these distances. It is this reliable long-range input that empowers safety systems to make faster, more accurate decisions in critical nighttime scenarios.
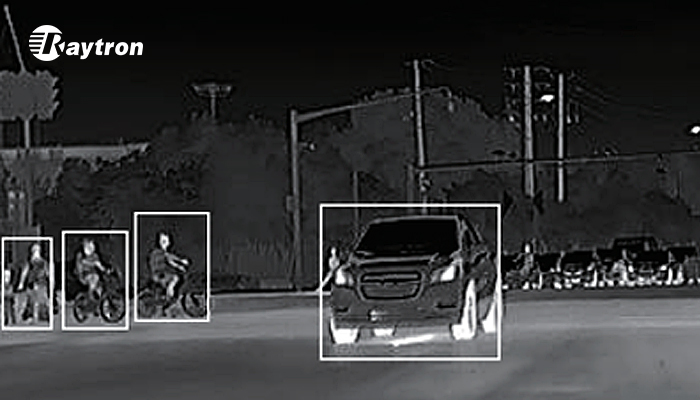

This superior detection capability is the foundation for more robust Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB/PAEB) and Forward Collision Warning (FCW) systems after dark. As noted by safety rating agencies like Euro NCAP, the weak nighttime performance of vision-based AEB is a known industry challenge. Thermal camera for ADAS integration directly addresses this by providing a reliable, all-weather detection layer for living objects. The consistent thermal data enables these critical systems to trigger earlier and with higher confidence in low-light scenarios where other sensors falter.
Furthermore, this makes thermal imaging a vital complementary sensor for the evolution toward autonomous vehicles (AV). For full self-driving systems to operate safely 24/7, they require redundant, diverse sensing modalities. For AI-powered thermal imaging for automotive safety, the high-contrast, consistent nature of thermal video streams allows machine learning algorithms to classify objects (pedestrian, cyclist, animal) with high accuracy and lower false-positive rates, building essential trust in automated systems.
Raytron's Role in Strategic Integration
A wide variety of forward-thinking automotive manufacturers and OEMs, including BYD, Geely, Zeek, Great Wall Motors, GAC Group, and more than 15 companies, are partnering with Raytron. Raytron's infrared thermal imaging technology features an ultra-long detection range of 300 meters. Now, the application is expanding from initial deployments in high-end off-road and intelligent driving platforms to a broader range of vehicle segments, as the industry prioritizes all-weather safety.

Incorporating such capabilities into real-world automotive systems is precisely the focus of industry innovators like Raytron. For instance, Raytron's Horus 640-D serves as a practical example of this technology in action. It is a compact LWIR (Long-Wave Infrared) thermal imaging module engineered specifically for automotive perception systems. Built upon Raytron's proprietary AEC-Q100–certified uncooled infrared detector, it is designed to deliver the reliable thermal data required for nighttime and low-visibility driving, all while meeting stringent automotive standards for durability, integration, and cost-efficiency. Its key advantages:
High-sensitivity detection of living objects
Consistent performance in total darkness or glare
All-weather robustness
The shutterless correction algorithm ensures continuous imaging
Low-power architecture, suitable for multi-sensor ADAS and autonomous driving stacks

About Raytron: Closing the Nighttime Safety Gap
As automotive thermal imaging establishes itself as the critical next frontier for reliable AEB and night driving safety, the industry’s ned has shifted from components to certified, automotive-ready perception systems. Through Raytron's vertically integrated industrial chain and AEC-Q100 certified technology, Raytron provides OEMs and autonomy developers with the strategic partnership and production-ready solutions needed to transform thermal imaging from an auxiliary feature into a core safety configuration. By collaborating with Raytron, forward-looking manufacturers gain more than a sensor supplier; they secure a partner committed to turning the promise of 24/7 safety and robust nighttime AEB into a deliverable reality for the vehicles of today and the autonomous fleets of tomorrow.